SOFTWARE
SinRX
Software for qualitative and quantitative analysis of energy dispersive X-ray Fluorescence (ED-XRF) spectra acquired on bulk and layered samples
GENERAL INFORMATION
- Runs on Windows 7, 8 or 10, both 32 and 64 bit;
- Analysis of spectra stored in different file formats such as mca, csv, spx, snx;
- Three possible levels of password protected access (end user, administrator, maintenance);
- Acquisition and analysis within just one software appplication.
SPECTRA ACQUISITION
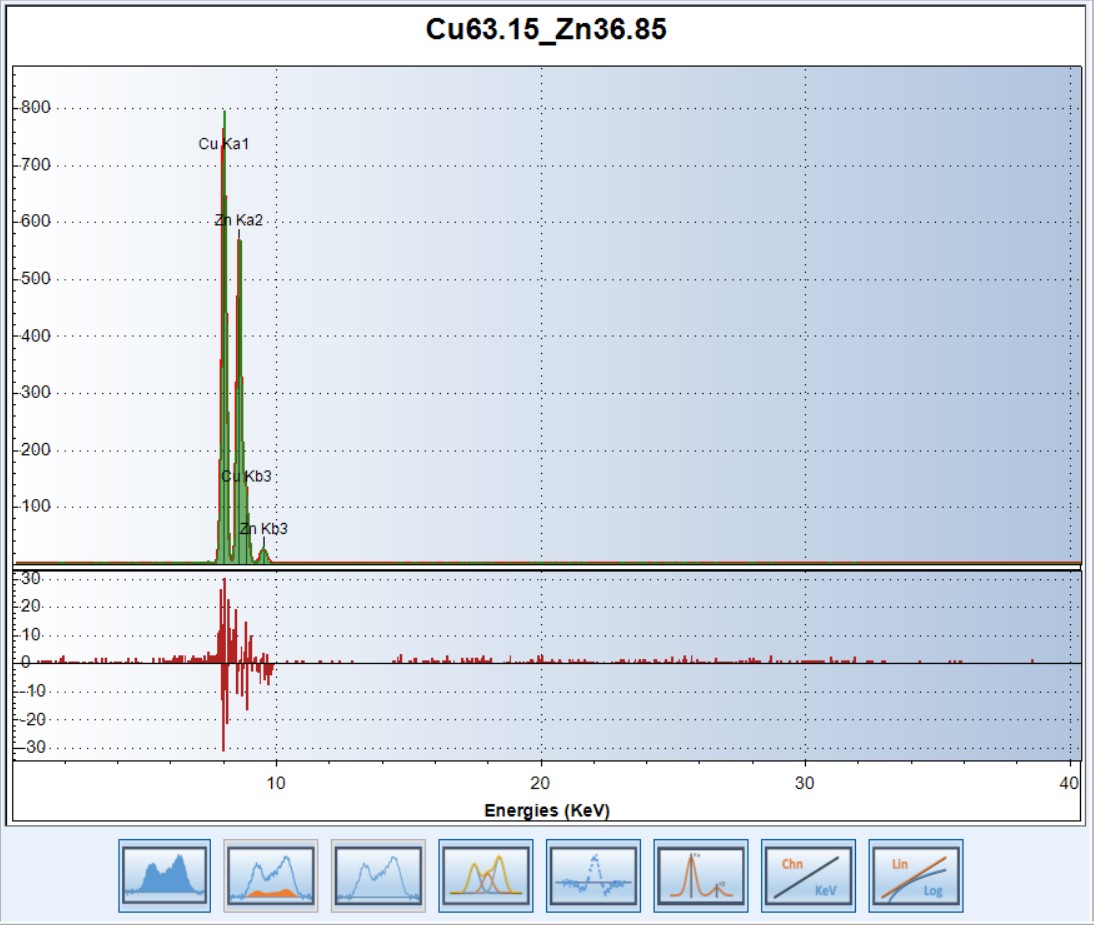
- Spectra acquisition from different models of DPP’s and by using different X-ray sources;
- Possibility to save the acquired spectra in different file formats (csv, snx);
- Display of: spectra in linear or logarithmic scaler; fit; background, residuals.
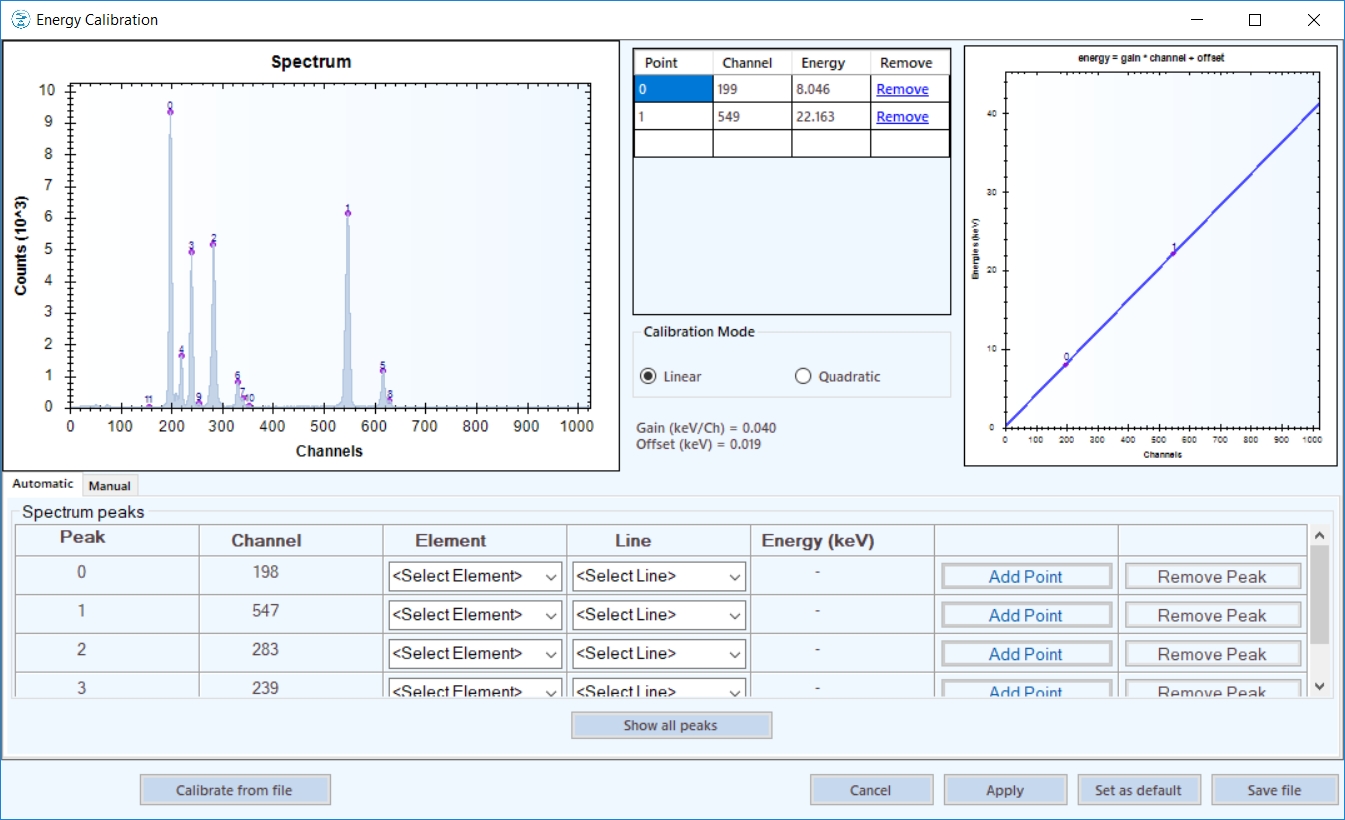
Calibration of the energy scale
- through automatic or manual peak identification, and linear regression.
Smoothing of the spectrum through:
- Savitzky-Golay filter;
- Moving average filter.
Background subtraction through:
- Orthogonal polynomials;
- Peak stripping.
SPECTRA ANALYSIS
QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
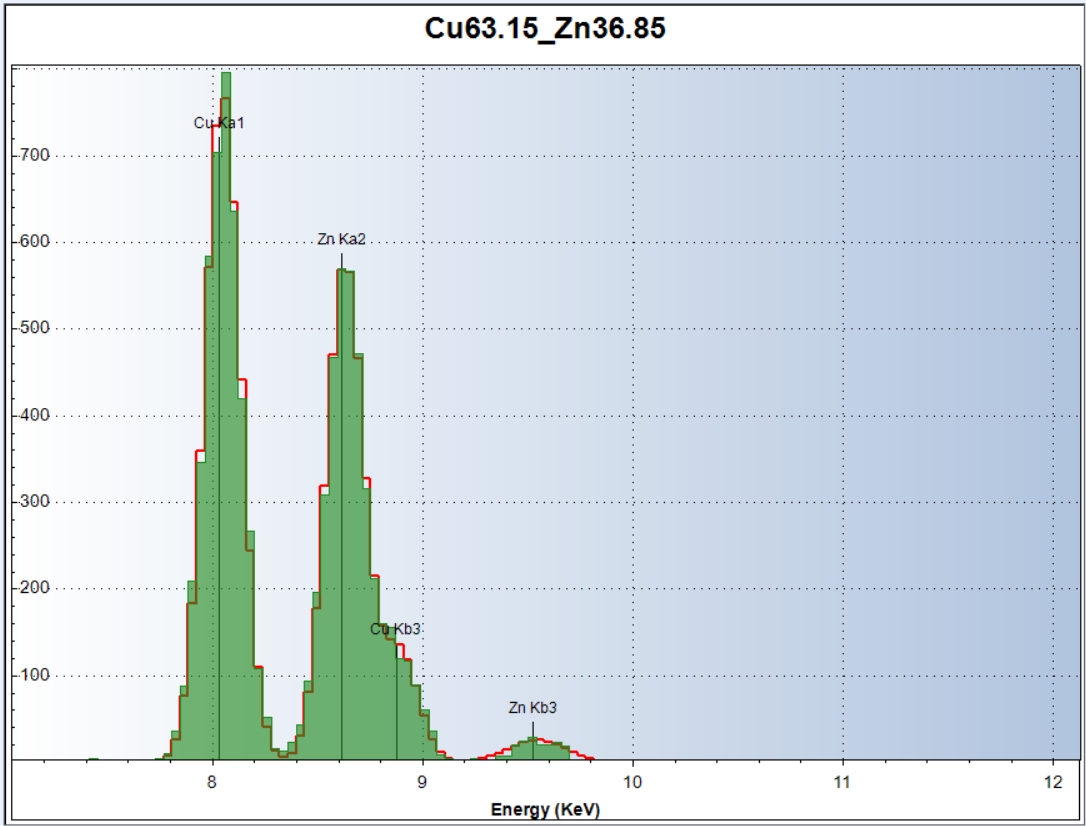
Fitting
- Trough gaussian curves using a Levenberg-Marqaart algorithm;
- Possibility to use modified gaussian curves to take into account the line shelf and tail.
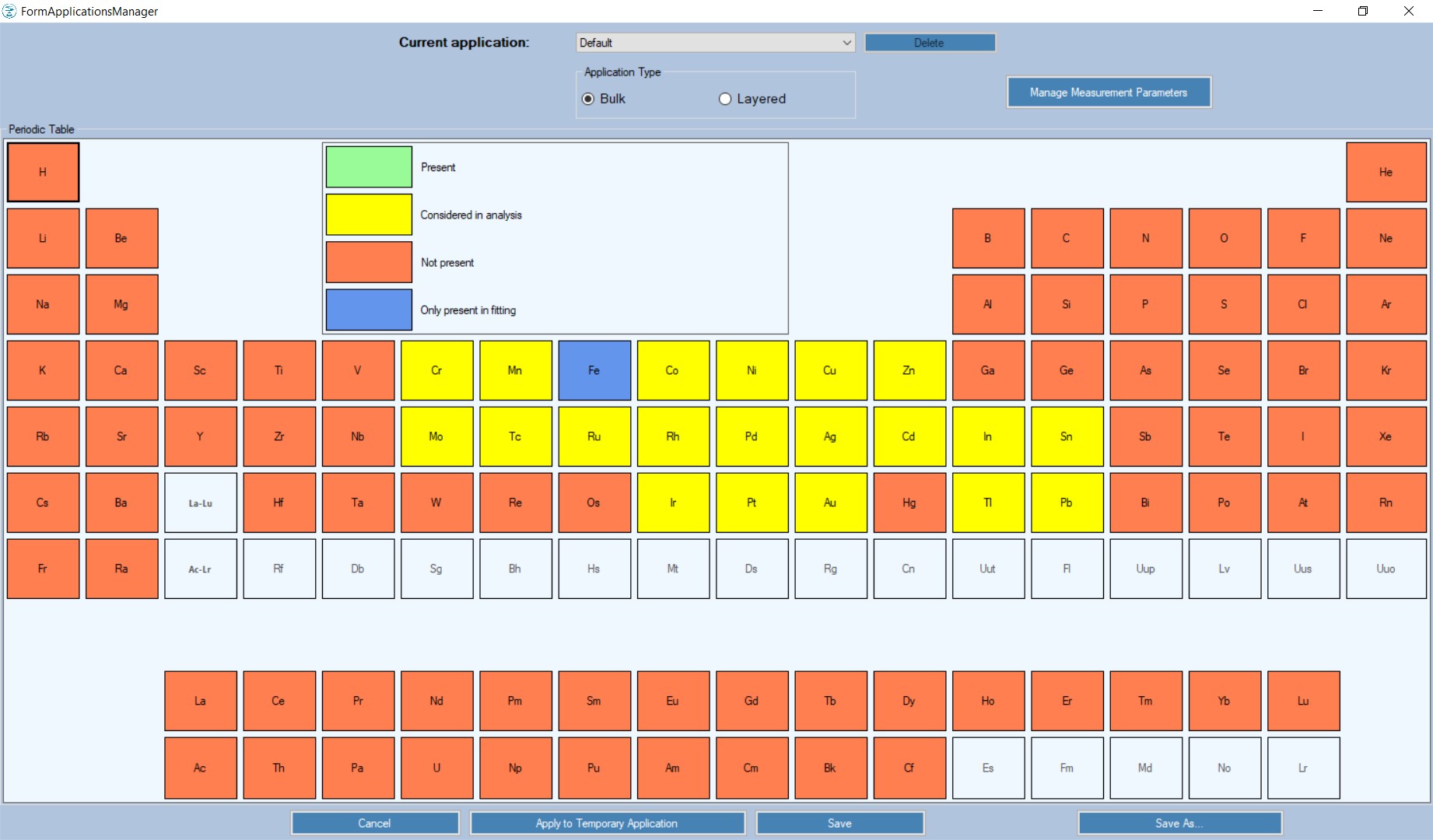
Automatic identification of elements through peak analysis:
- blacklist of elements to avoid misidentification;
- manual adjustments of composition;
- automatic identification of “sum” and “escape” peaks.
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
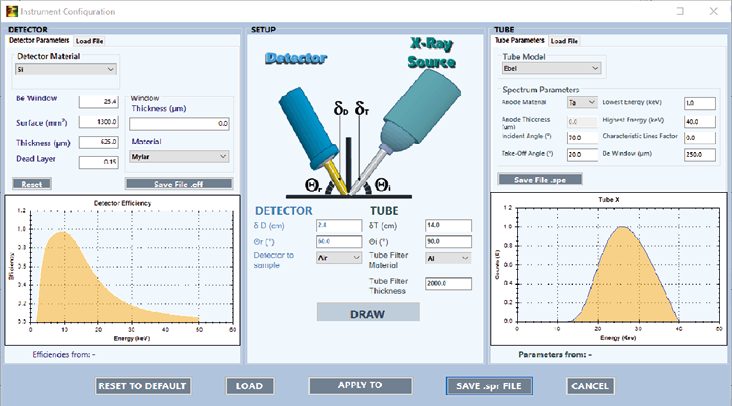
Standardless - fundamental parameters of:
- Different tube spectra models available (for both end-window and side-window X-ray tubes);
- Detector efficiency spectrum adjustable by the user;
- Possibility to choose and save the geometry of analysis.
Analysis with standards:
- Empirical calibration curves (linear and quadratic models), with or without interelement corrections;
- Lucas-Tooth algorithm;
- Lachance-Traill algorithm;
- Modified fundamental parameters analysis to take into account the results on standard sample;
- Combined methods: FP + empirical calibration.
FURTHER ANALYSIS AND REPORT
Smart analysis:
for the rapid identification of the material, with possibility of creating a customized database of materials.
Matching analysis:
suggests, among all samples saved in the database, the one whose spectrum has the greatest likeness to the sample under analysis.
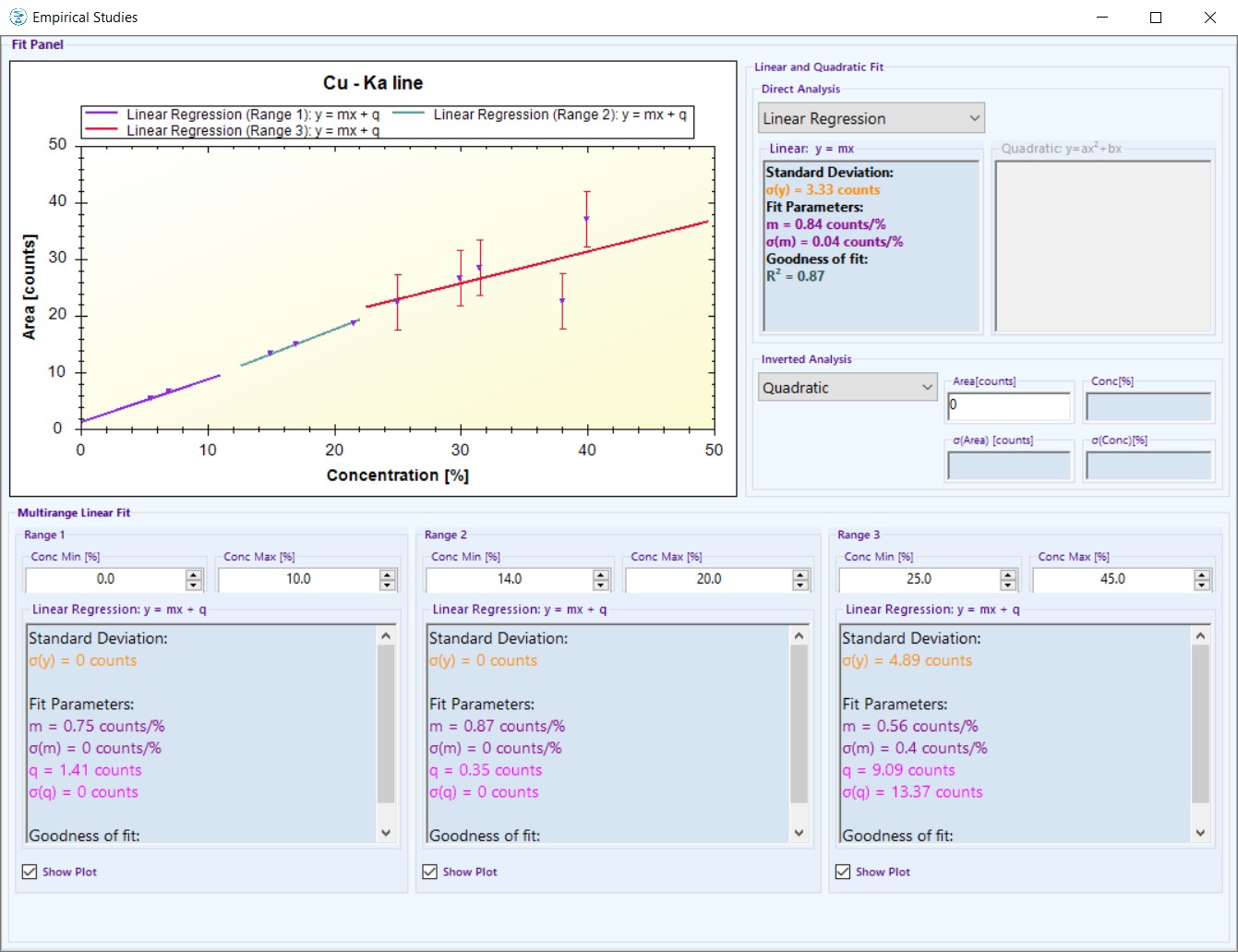
Empirical Studies:
- Displaying of elements concentrations vs. corresponding peak areas;
- Linear or quadratic fit of the points;
- Inverse analysis to determine the concentration of the elements of an unknown sample.
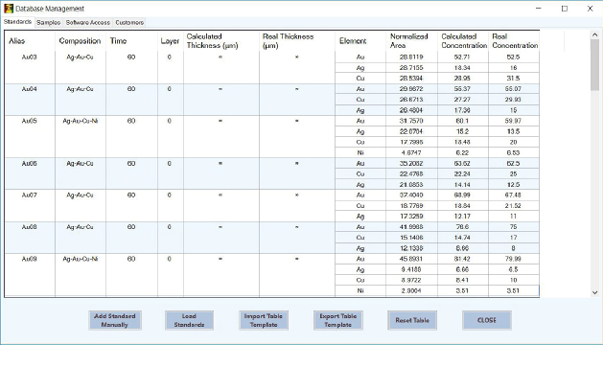
Report and databases
- Database of customers and samples;
- Database of reference materials;
- Database of standard samples for quantitative analysis;
- Database of users;
- Database of applications for optimized analysis
- Creation of customized reports.